The Facts
about BMI
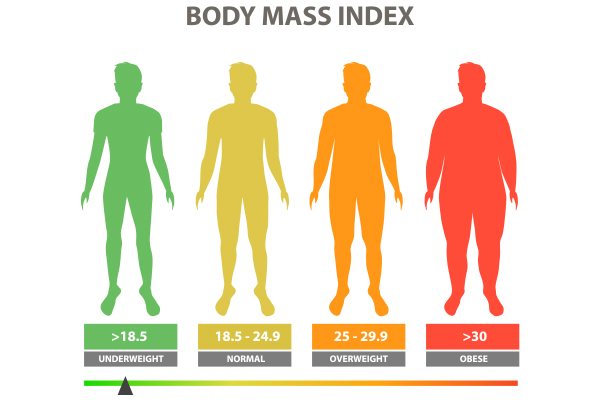
BMI
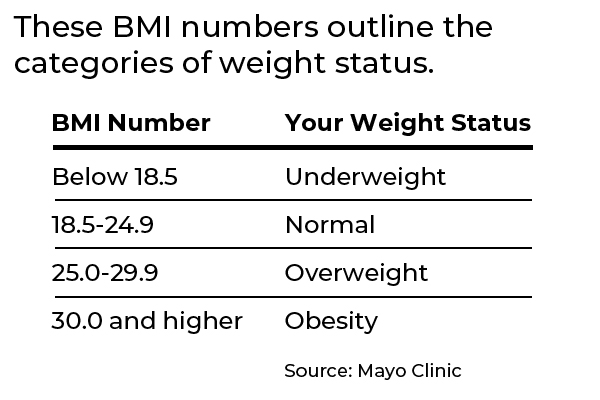
Body mass index (BMI) is a person’s weight divided by the square of height. A high BMI can indicate high body fat. BMI screens for weight categories and is often used to diagnose obesity.
To calculate BMI, you can also multiply your weight in pounds by 703, then divide by your height in inches and then divide again by your height in inches.
For example, if someone is 5’8” and weighs 200 lbs The BMI reading would be 30.4 which would put the person in the obese category.
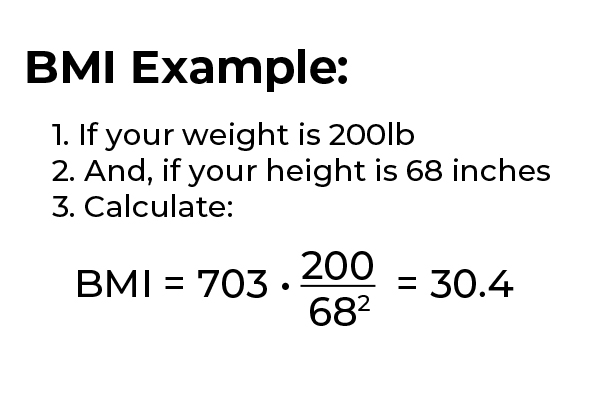
What is obesity and why is excessive weight so dangerous to one’s health?
Obesity is a complex medical condition that increases the risk of other serious diseases and health problems, including:
- Type 2 diabetes. Obesity can impact the way your body uses insulin to control your blood sugar levels. Obesity raises the risk of insulin resistance. Uncontrolled diabetes can be life-threatening.
- Cancers. Obesity may increase the risk of cancer of the uterus, cervix, endometrium, ovary, breast, colon, rectum, esophagus, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidney and prostate.
- Heart disease and strokes. Obesity increases the likelihood of high blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels. Both are risk factors for heart disease and strokes.
- Digestive problems. Obesity increases the likelihood of developing liver problems, gallbladder diseases and heartburn. Sleep apnea. Obesity increases the likelihood of sleep apnea in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep.
- Osteoarthritis. Obesity can increase inflammation throughout the body along with increased stress placed on weight-bearing joints. Both of these conditions can lead to complications such as osteoarthritis.
- Severe COVID-19 symptoms. Obesity increases the likelihood of developing severe COVID symptoms if you become infected.
The good news is that even modest weight loss of 5% (10 lbs in a 200 lb patient) can prevent or improve the health risks associated with excessive weight. With a healthier diet, increased physical activity, and lifestyle changes, you can lose weight and keep it off. Prescription medications and weight-loss surgery such as bariatric surgery are additional tools used for treating obesity.
Achieving and maintaining maintaining a healthier weight is not easy
It is no secret that weight loss can be very hard work. And maintaining weight loss can be equally challenging. If both were easy, there would be far fewer people across the globe struggling with weight loss and weight management. On the contrary, millions and millions of people across the globe are overweight.
While the general principle for weight loss seems straightforward–reduce calorie intake from food and beverages and burn more calories than you take in with physical and daily activities–we all know it is not that simple.
We also know that millions of people in Western, developed societies consume far too many calories from fast foods, snacks, processed foods, and high-calorie beverages such as sodas, fruit drinks, and alcohol. A lot of us also sit at sedentary jobs, drive instead of walk, order online instead of walking around to stop, and spend a lot of time with a remote control while drinking and eating as a form of relaxation. With all these modern habits, it is easy to understand why so many people struggle with weight.
In addition to these lifestyle challenges, there are many complex medical reasons why people have difficulty losing weight and keeping it off. Obesity can result from many variables, including heredity, physiological, and environmental factors.
LifeStyle Medical Centers is here to help with all of these challenges. We are committed to helping you lose weight with a sustainable, effective program that includes a team of experienced experts, digital tools to track your daily efforts and progress, medications when needed, and on-going support.
Sources:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, https://www.cdc.gov/.
- Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health.
- Cleveland Clinic, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases.
