Medication Management
Prescription Weight Loss Medications
Qsymia (phentermine-topiramate)
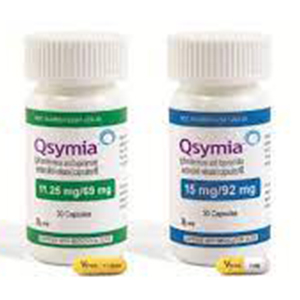
Qsymia (phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule) is a prescription weight loss drug developed by the pharmaceutical company VIVUS for patients with obesity who have not been able to lose enough weight with diet and exercise alone to improve their health.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Qsymia in July 2012 for chronic weight management in adults with an initial BMI of 30 kg/m2 or greater (obese) or 27 kg/m2 or greater (overweight) with at least one weight-related comorbidity such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or dyslipidemia. Like all other prescription weight-loss medications, it should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider and as part of a care program that includes a healthy reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity. It has been approved for long-term use.
Qsymia is given in capsule form with extended-release and is taken with a glass of water with or without food once a day in the morning.

How does Qsymia work for weight loss?
Qsymia is a combination of two medications. The phentermine component is a sympathomimetic amine that mimics neurotransmitters in the brain to reduce hunger. It was first approved by the FDA to help with weight loss over 60 years ago.
The other component is topiramate, which was approved by the FDA over 20 years ago to treat epilepsy and later found to help with weight loss. It works on different neurotransmitters in the brain than phentermine to decrease appetite and increase feelings of fullness after eating. Together these two drugs promote weight loss by making it easier to follow a reduced-calorie diet, and are much more effective together than either one alone.
What are the clinical trial weight loss results for Qsymia?
In one large clinical trial, 2487 overweight or obese patients were randomized to receive placebo, mid dose Qsymia, or full dose Qsymia. All patients participated in a standardized lifestyle program. After 56 weeks weight loss averaged 1.2% in the placebo group, 7.8% in the mid dose group, and 9.8% in the full dose group.(1) In addition, patients receiving Qsymia had greater improvements in waist circumference, blood pressure, blood glucose, and cholesterol than the placebo group.
It is important to note that these impressive amounts of weight loss occurred over 52 weeks of treatment. Keep this in mind when you read about some ‘miracle’ treatment that claims huge amounts of weight loss in a very short time.
What are the health benefits of Qsymia?
Qsymia can help people with obesity to first lose weight, and then help with the second very important step of maintaining the healthier weight. Doing so has numerous health benefits.
The health risks that can accompany obesity are well known, and include heart disease, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, stroke, certain types of cancer, and a shortened life span. In pre-menopausal women, obesity is also associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition characterized by hormonal changes resulting in such things as irregular menses, difficulty getting pregnant, and excess body hair.
Losing weight can prevent, treat, and in some cases even reverse obesity-related health conditions. It is important to note that a patient does not have to become ‘slender’ to benefit from weight loss; just 5-10% (10-20 lbs in a 200 lb person) can result in very significant health improvements, including lowering blood pressure, lipids, blood glucose, and hemoglobin A1c. There can also be physical benefits (more energy, better mobility, diminished joint pains) and mental/emotional benefits (diminished stress and anxiety, increased confidence and self-esteem).
Who is a good candidate for Qsymia?
Qsymia is typically prescribed to people who have:
- BMI of 30 or higher
- BMI of 27 or higher with other weight-related health problems such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or type 2 diabetes
Qsymia should not be taken by persons with an overactive thyroid gland, glaucoma, or taking a monoamine oxidase type of antidepressant medication. It also is not for women who are pregnant or may become pregnant, as Qsymia can cause fetal harm.
Before prescribing Qsymia or any other weight loss medication, your healthcare provider will carry out a thorough medical evaluation to determine if the medication is suitable for you. Medications may adversely interact with each other; always tell your healthcare provider about all your prescription and non-prescription medications when considering whether to start a new medication.
What are the possible side effects of Qsymia?
As with any medication, Qsymia carries some risks and potential side effects. The most common side effects of Qsymia include dry mouth, dizziness, paresthesia (tingling sensation), headache, constipation, increased heart rate and/or blood pressure, difficulty sleeping, and mood changes. Side effects are often mild and go away within a few days. If you have any questions or concerns about possible side effects, be sure to promptly contact your healthcare provider.
Is there any risk of abuse or dependency?
The phentermine component of Qsymia has some stimulant properties and is therefore classified as a Schedule IV medication, meaning low potential risk for abuse or dependence. Examples of other Schedule IV drugs include Xanax, Darvocet, Valium, Ambien, and Tramadol.
How is Qsymia taken?
Qsymia should be taken by mouth with a glass of water, typically once a day. Avoid taking this medicine in the evening since one possible side effect is that it may interfere with sleep.
Do not stop taking Qsymia without first consulting your healthcare provider since if taken at higher doses the medication is best discontinued gradually.
What if I miss taking a dose of my Qsymia pills?
If you miss a dose, you should just skip it for that day and resume at your normal time the next day. Never take extra doses or 2 doses at the same to make up for the missed dose.
What happens when I stop taking Qsympia?

It is an unfortunate fact that most people who lose weight regain much or all of the weight that they lost. On the one hand, this should be expected if after losing weight someone stops everything they did to lose weight and goes back to doing everything exactly as they did while gaining weight.
However, making very important lifestyle changes like eating a healthy diet and getting more physically active often are not enough to prevent regaining weight. The reason for this is that when you have obesity, the regulation of your body weight is dysfunctional. Your body will try to push you back to your previous weight. In this situation, Qsympia or some other long-term weight loss medication may be a necessary part of the care plan needed to keep your weight in a healthier place.
It is as important to work with your health care provider after a weight loss program as it is during the weight loss program!
Footnote:
- National Library of Medicine, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3626409/
Sources:
Are you ready to start down the path to a healthier you?
Prevent, reverse, or manage a chronic disease?
Take control of your health today. Better health IS within your reach.
Take the first step today. Call us today @ (919)354-7077
Take The Stress Out Of Prior Authorizations
We will work with you, your insurance company, and pharmacy to get your medication needs met.

